 DFG Walter-Benjamin Post Doc @ Bielefeld University
DFG Walter-Benjamin Post Doc @ Bielefeld UniversityPost Doc, Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology, CH.
Hi! I'm Gaurav Baruah, a DFG Walter-Benjamin Postdoc at Bielefeld University in the Theoretical Biology group. I'm currently working on several research projects, including adaptive species rewiring, eco-evolutionary feedbacks on the resilience of mutualistic networks, bringing collapsed ecological networks back to life, the evolutionary impact of competition on species coexistence, and the evolution of partial migration. All of these are theoretical studies, but I'm using publicly available data from different databases for empirical insights.

Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "Education
-
 University of ZurichPhD in EcologySep. 2015 - Feb. 2020
University of ZurichPhD in EcologySep. 2015 - Feb. 2020 -
 IISER KolkataIntegrated BS & MS in BiologyAug. 2010 - May. 2015
IISER KolkataIntegrated BS & MS in BiologyAug. 2010 - May. 2015
Experience
-
 University of Toronto, CanadaSummer Research InternMay. 2014 - Aug. 2014
University of Toronto, CanadaSummer Research InternMay. 2014 - Aug. 2014
Grants & Awards
-
Faculty of Biology Small Experimental Grant2023
-
DFG Walter-Benjamin Research Grant2023
-
Alexander von Humboldt Post Doctoral Fellowship2023
-
UZH Forschungskredit Research Grant2019
-
DST Inspire Fellowship2010
-
OIL India scholarship2007
News
Selected Publications (view all )
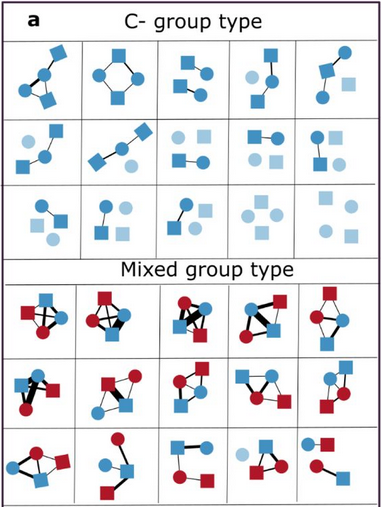
Plant metabolites modulate animal social networks and lifespan
Pragya Singh, Leon Brueggemann, Steven Janz, Yasmina Saidi, Gaurav Baruah, Caroline Müller
Journal of Animal Ecology (in press) 2024 New
Social interactions are prevalent in animals, with some individuals participating in more interactions than others. However, the mechanisms underlying this heterogeneity in social interaction frequency and its potential fitness consequences remain poorly characterized. Here, we examine the effects of non-nutritive plant metabolites ("clerodanoids") on social networks and lifespan in the turnip sawfly. ...

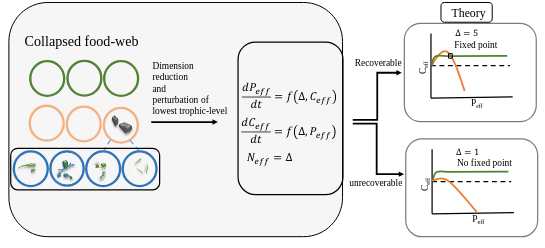
Predicting recoverability of collapsed food webs through perturbation and dimension reduction
Swastik Patnaik, Gaurav Baruah
bioRxiv 2024
Biodiversity collapse, driven by escalating environmental changes, poses significant threats to ecosystem stability and the provision of essential ecosystem services. Understanding the recoverability of collapsed food webs thus is crucial for devising effective conservation strategies. This study delves into the theoretical exploration of the recoverability of food webs from a collapsed state. Through simple tools like dimension reduction, propagation of species-specific perturbation, and dynamical simulations, we explore whether simple tri-trophic food webs can be recovered from a collapsed state. Our study examines in detail the topological features of predator-prey food webs that could either facilitate or impede their recovery....

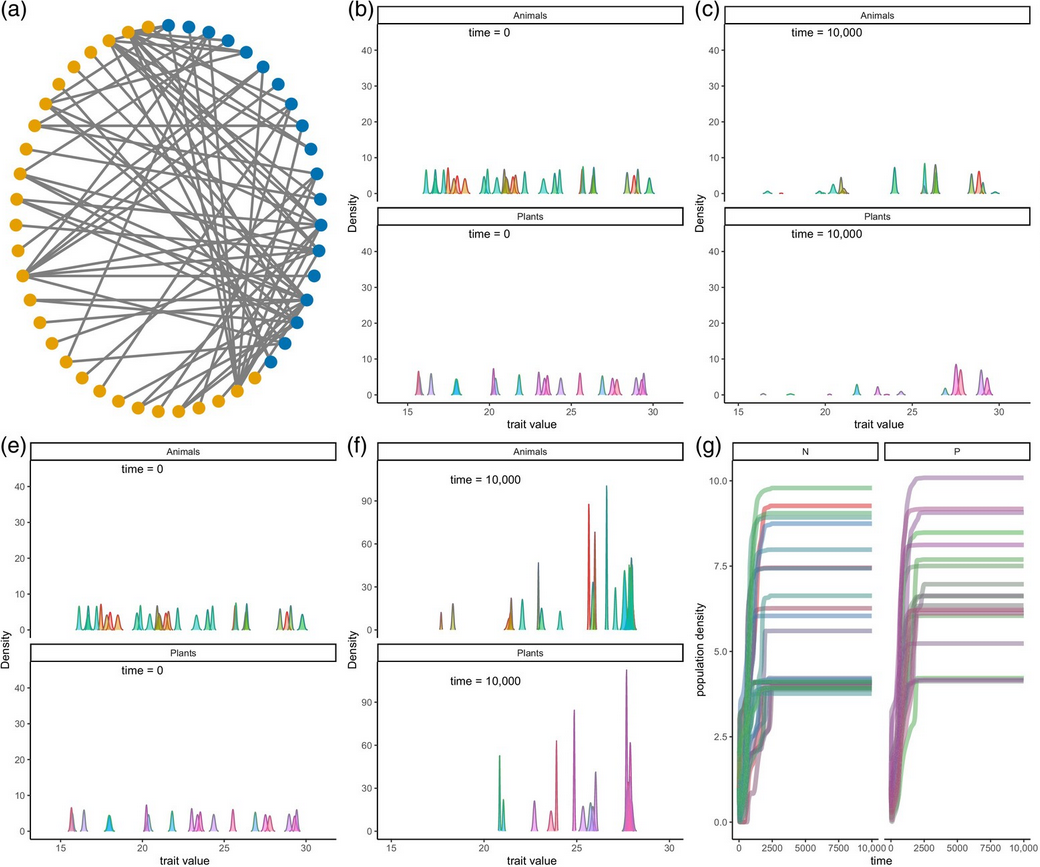
Stability, resilience and eco-evolutionary feedbacks of mutualistic networks to rising temperature
Gaurav Baruah, Tim Lakaemper
Journal of Animal Ecology 2024 New
Ecological networks comprising of mutualistic interactions can suddenly transition to undesirable states, such as collapse, due to small changes in environmental conditions such as a rise in local environmental temperature. However, little is known about the capacity of such interaction networks to adapt to a rise in temperature and the occurrence of critical transitions....

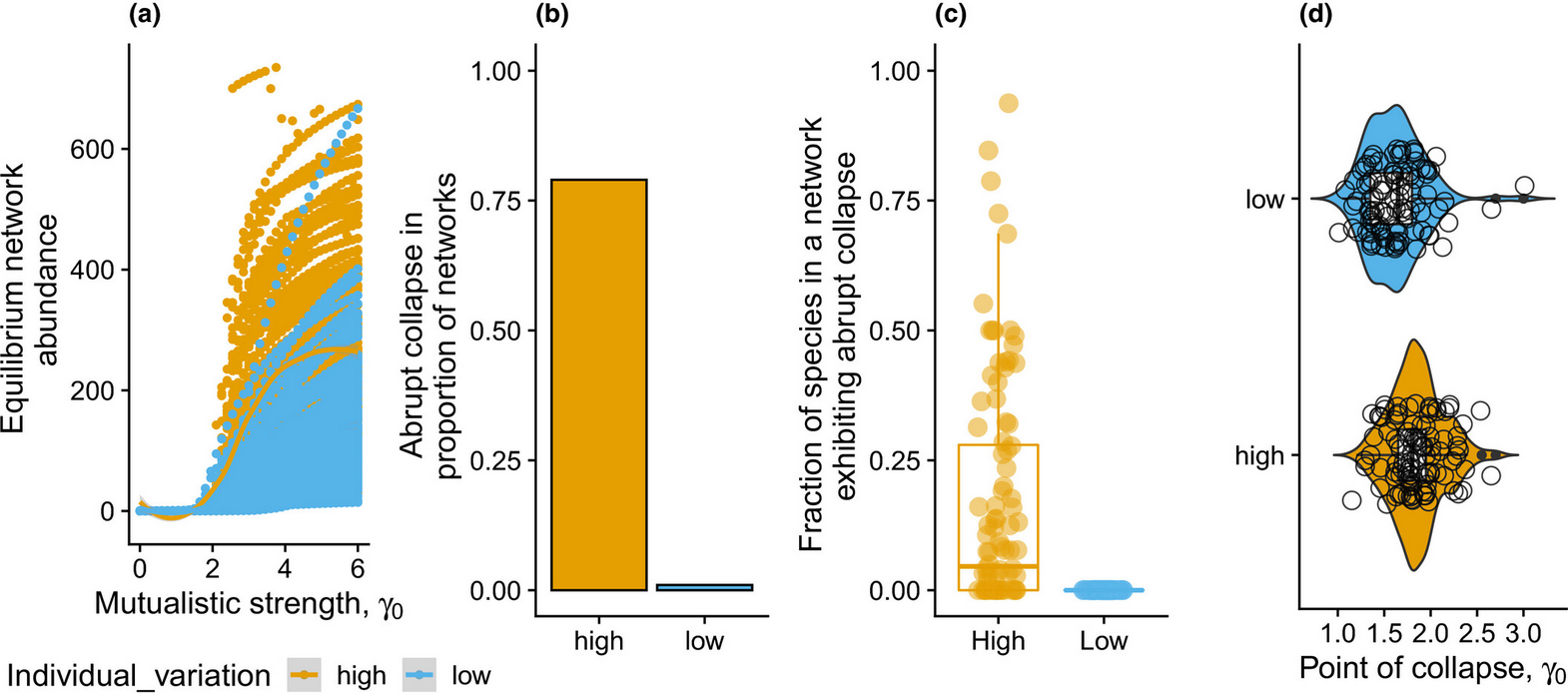
The impact of individual variation on abrupt collapses in mutualistic networks
Gaurav Baruah
Ecology Letters 2022
Individual variation is central to species involved in complex interactions with others in an ecological system. Such ecological systems could exhibit tipping points in response to changes in the environment, consequently leading to abrupt transitions to alternative, often less desirable states. However, little is known about how individual trait variation could influence the timing and occurrence of abrupt transitions. Using 101 empirical mutualistic networks, I model the eco-evolutionary dynamics of such networks in response to gradual changes in strength of co-evolutionary interactions...
